Investment Focus: Clean Energy
Opportunities amid market correction as global demand surges
21 Feb, 2025
The Earth is experiencing unprecedented warming, with global surface temperatures now 1.2°C higher than pre-Industrial Revolution levels of the late 1800s - a peak not seen in over 100,000 years, according to the UN.[1] This warming has accelerated dramatically, with 2011-2020 marking the hottest decade ever recorded. Scientists now widely agree that human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels like coal, gas, and oil, are driving this temperature rise.

Growing energy demand and market drivers
To address this crisis, we must fundamentally transform how we generate and consume energy, shifting toward lower-carbon alternatives. This massive undertaking, known as the 'energy transition,' requires substantial infrastructure investments and a complete reimagining of power generation systems.
Part of the problem is that energy demand continues to grow. There is the usual growth in demand that comes from global economic expansion, but now there is demand emerging from fast-growing markets such as China and India. There is also demand emerging from the growth of AI. It takes enormous reserves of energy to store and analyse the data necessary for AI insights. It is estimated that a search query through ChatGPT requires around 10x the energy of one using Google.[2]
The energy transition is largely focused on electrification - replacing fossil fuel technologies with electric alternatives. Since electricity can be generated through renewable sources like solar and wind power, this shift away from oil and gas helps reduce carbon emissions. However, this transformation requires massive infrastructure development, including new wind farms and solar installations, along with upgraded power grids to deliver electricity from generation sites to end users and handle increased demand.
The International Energy Agency says global electricity demand grew by around 4% in 2024, up from 2.5% in 2023. This would represent the highest annual growth rate since 2007, excluding the exceptional revival in demand seen after the pandemic and global financial crisis. The strong increase in global electricity consumption is set to continue into 2025, with growth forecasted around 4%.[3]
Global policy support and investment
Around 90% of the world’s GDP is now under a net zero target.[4] Governments are supporting the shift to green energy, with UK government stating an explicit target to achieve clean power by 2030 and accelerate to net zero. This includes the launch of Great British Energy, which aims to support clean energy industries, funding for carbon capture projects and clean energy generation.
These commitments are mirrored all over the world: India, for example, added 14% of renewable capacity in 2024 alone. Renewable energy now accounts for over 43% of India’s installed power generation capacity.[5] China’s growth in solar and wind power means it will have half of the world’s renewables by 2030.[6] While Donald Trump has pared back spending on green energy initiatives, the US still spent $239bn in 2023, up 38% from 2022.[7]
Investment opportunities in clean energy
There are a range of ways to invest in clean energy.
1. Pure play renewables
The ‘purest’ approach is to target green energy providers. These are wind farm groups or solar panel makers. There are other forms of energy emerging – such as hydrogen, but they are generally at an early stage. The major listed companies are groups such as Orsted, Vestas Wind Systems or First Solar.
Investors can gain direct exposure to renewable energy through specialised Investment Trusts like Greencoat Renewables and Foresight Solar. These trusts hold portfolios of renewable energy assets that vary by development stage (from early-phase projects to operational facilities), geographic location, and technology type (including wind, solar, and hydrogen installations).
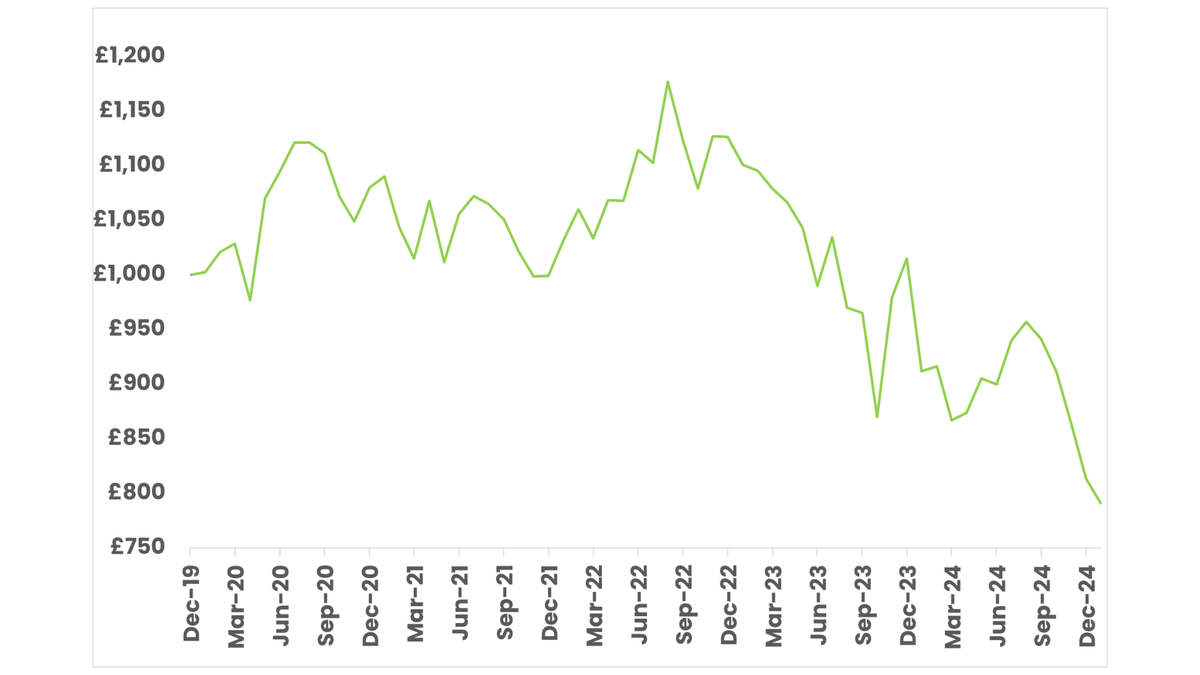
5 year performance of Greencoat Renewables. Source: FE Fund Info.
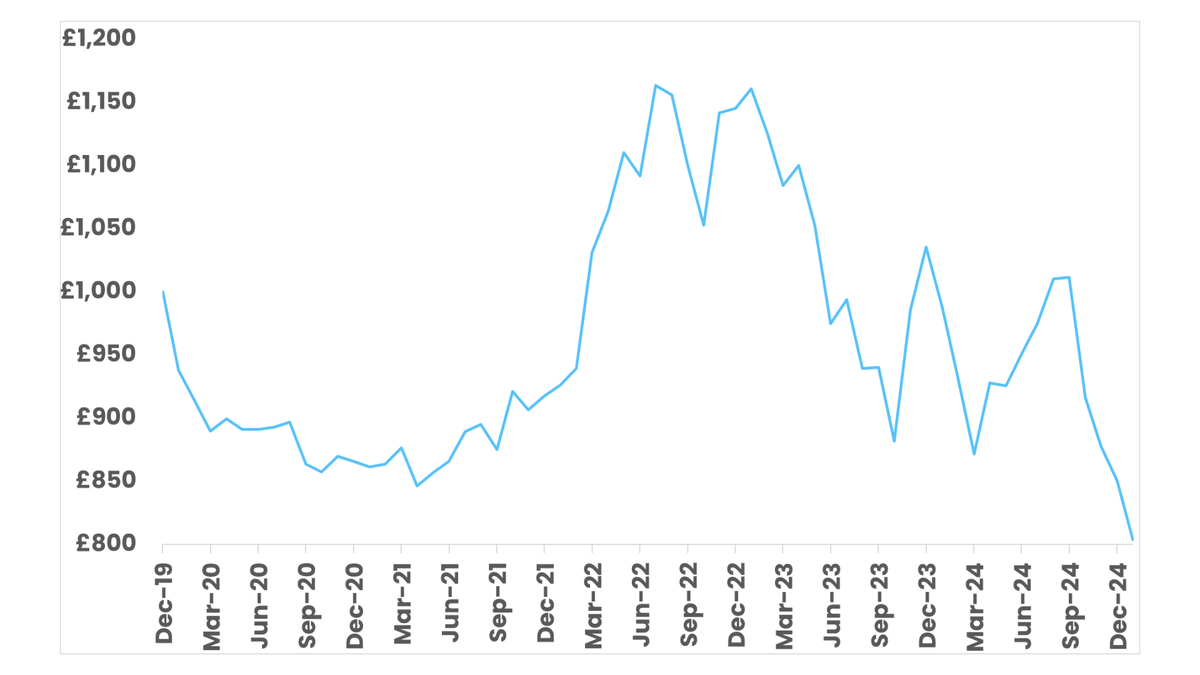
5 year performance of Foresight Solar. Source: FE Fund Info.
2. Infrastructure
It is also possible to invest in listed energy infrastructure providers. That might be groups such as National Grid, which recently launched its ‘great grid upgrade’. It is responding to increases in demand for electricity with a restructuring of the national electricity network, including new wires, cables and pylons. This is addressing the problem that electricity is increasingly generated offshore (wind) or in remote parts of the UK (solar) and it needs to move to the areas of greatest demand, particularly the UK’s major cities. Across the world, energy infrastructure is undergoing a similar replumbing.
3. Battery storage
There is also the battery storage element. Inevitably, the wind doesn’t always blow and the sun doesn’t always shine. Battery storage needs to be in place to deal with this intermittency. Increasingly, batteries are being installed within national grids to store energy for use at a later stage. This will reduce reliance on ‘emergency’ sources of energy.
4. Technology providers
Within these broad categories, there are also a range of suppliers, technology providers, and other ancillary services where people can invest. For example, there will be technology providers that help businesses use resources more efficiently, monitoring energy or water use. There are also carbon capture options, which look to take carbon out of the atmosphere to help with net zero targets.
One murkier element is that some of the most exciting businesses will sit within the fossil fuel providers. BP, for example, owns Chargemaster, the electric car charging network in the UK (now BP Pulse). Many fossil fuel companies also have wind farms and solar businesses. In general, collective funds that focus on clean energy will want to see more than half of a company’s revenues coming from clean energy before they are willing to invest.
There are a range of collective funds investing in the sector. There are diversified ‘environmental’ funds, such as Impax Environmental Markets, or dedicated clean energy funds, such as the Schroder Global Energy Transition fund, or passive options, such as the iShares Global Clean Energy ETF. There are niche funds focusing on battery storage, such as the Gresham House Energy Storage or Gore Street Energy Storage funds, alongside the renewable infrastructure Investment Trusts.
Market performance and valuations
The clean energy sector has been through a significant boom and bust in recent years. During the pandemic and after the war in Ukraine disrupted fossil fuel energy supplies, it appeared likely that governments across the world would expand their green energy initiatives. The iShares Global Clean Energy ETF, often seen as a bellwether for the sector, soared 43.7% in 2019 and another 140% in 2020. Since then, there has been an uncomfortable unwinding of this exuberance – the ETF has dropped 24.1% in 2021, 5.6% in 2022, 20.5% in 2023 and 26.1% in 2024.
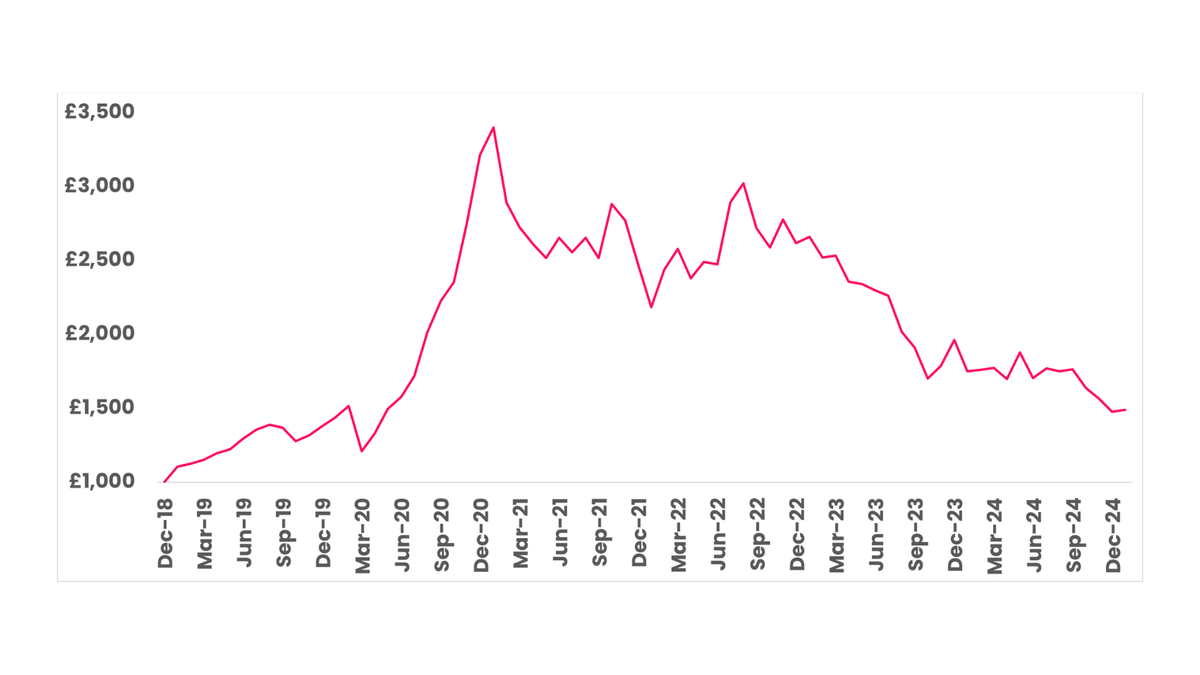
iShares Global Clean Energy ETF. Source: FE Fund Info.
Industry challenges and solutions
There have also been some well-documented problems for parts of the renewable energy industry. Wind farms have struggled with rising costs and higher interest rates, while solar energy has been hit by increasing commoditisation and cheap imports from China.
Nevertheless, the long-term trend towards renewables appears inexorable. It is well-supported by policymakers across the world, and backed by government spending. Robeco recently highlighted it as one of the nine trends likely to reshape portfolios in the year ahead. It said:
Global electricity demand is accelerating, highlighting the urgency of expanding infrastructure. The IEA projects that power consumption from data centers, AI, and cryptocurrency could double by 2026. In the near term, renewables, gas, and storage solutions are the best technologies to meet this surge in demand.
Meanwhile, energy security is high on the political agenda, and government incentives for clean energy infrastructure are spurring new construction projects to upgrade energy systems and modernize the grid. Global policy goals include tripling renewable energy and doubling efficiency by 2030. The Inflation Reduction Act supports US efforts, while the EU’s REPower Plan and Green Deal underpin Europe’s energy shift…Furthermore, growing power demand, driven by data center build-out, favors low-carbon, low-cost electricity developers/utilities.
It is also the case that the sector now looks cheap relative to its history, and to other major growth themes such as artificial intelligence. In the renewable energy infrastructure sector, there are attractive dividends available. Eight out of the 20 Investment Trusts in the sector are paying a dividend of over 10%. Many of the problems in the sector appear to be behind it.
Below are 15 Investment Trusts with environmental or sustainable focuses, spanning renewable energy, storage infrastructure, and eco-conscious companies.
Investment Trust |
Gresham House Energy Storage Fund Plc |
Impax Environmental Markets Plc |
JLEN Environmental Assets Group Ltd |
Jupiter Green Investment Trust Plc |
Greencoat UK Wind Plc |
Greencoat Renewables Plc |
Gore Street Energy Storage Fund |
Foresight Solar Fund Limited |
Bluefield Solar Income Fund |
NextEnergy Solar Fund Limited |
SDCL Energy Efficiency Income Trust Plc |
The Renewable Infrastructure Group |
Foresight Solar & Technology VCT Plc |
Gresham House Renewable Energy VCT 1/2 Plc |
Source: Green Finance Guide.
Capital at Risk: Review each trust's portfolio to ensure it matches your definition of sustainable investing. Past performance is not a guide to future returns and your capital is at risk.

Political risk assessment
Part of the reason for the recent weakness in share prices has undoubtedly been the Donald Trump factor. His skepticism toward climate change, including his withdrawal from the Paris Climate Agreement (twice), rollback of carbon emission regulations and fuel efficiency standards, and his recent dismissal of climate concerns as "alarmist" have impacted market sentiment. His appointment of Liberty Energy CEO Chris Wright as energy secretary further signals his administration's pro-fossil fuel stance.
However, it is debatable whether he will roll back the previous administration’s landmark climate funding bill, the Inflation Reduction Act, in full. Research from the Net Zero Industrial Policy Lab found that full repeal of the IRA would, in the most likely scenario, “harm US manufacturing and trade and create up to $80 billion in investment opportunities for other countries, including major US competitors like China. US harm would come in the form of lost factories, lost jobs, lost tax revenue, and up to $50 billion in lost exports.”
Goldman Sachs points out that the bill has delivered around $3 trillion in clean energy spending.
Opportunities for investors
The move towards clean energy remains a megatrend in spite of the recent wobble in share prices. There are risks, however, share prices today appear to reflect that risk, and there are some attractive dividend yields available across the sector. Investors can also reflect that their savings are helping to fight climate change.
For those looking to participate in this trend, several investment approaches are available:
Passive investment options
Active investment options
Active funds can be less volatile. They can vary allocation to different clean energy themes, depending on valuations, and have generally protected investors against some of the highs and lows of this part of the market.
Investment Trusts for direct infrastructure exposure
Investment trusts can offer a different type of exposure. They can hold renewable energy infrastructure assets directly rather than through listed companies.
There are plenty of choices in the AIC Renewable Energy Sector, including:
Battery storage options
There are also battery storage options as per the ones below with attractive income yields:
---
[1] UN, March 2024
[2] AIC, May 2024
[3] IEA, July 2024
[4] Net Zero Standard, February 2025
[5] Economic Times , January 2025
[6] The Guardian, October 2024
[7] BBC, April 2024
[8] BBC, January 2020



